










NP 120 Part II
Microbiome and Mental Health
Exploring the Role of Microbiota from Neurodevelopment to Neurodegeneration
Course Overview
This course builds upon the foundation established in NP 120 Part I, Microbes in Our Gut: An Evolutionary Journey into the World of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis and Diet-Mental Health Relationship (DMHR).
Welcome to NP 120 Part II! As a successful NP 120 Part I graduate, you’ve already delved into the micro-universe within our bodies known as the microbiota-gut-brain axis (MGBA). You’ve gained a solid understanding of the MGBA’s historical significance, its tiny inhabitants called microbiota, and the research methods used in exploring its existence. You’ve unraveled the secrets of these creatures’ composition and abundance, explored the intricate communication pathways connecting them with our gut, brain, and other body systems, and discovered how these various systems each play a vital role in the functioning of this universe.
You’re ready to leap into the intricate mechanisms interconnecting the microbiota-gut-brain axis with the diet-mental health relationship (MGBA-DMHR). In this course, you’ll venture deeper to unlock these mechanisms and gain a front-row seat in understanding how they shape our everyday human experience. You’ll learn how certain foods contain keys to unlocking these mechanisms, shaping our moods, emotions, psychological experience, social functioning, and even how they influence our dietary intake behavior. In this course, you’ll gain knowledge of the MGBA-DMHR’s intimate role in the development of psychological, psychiatric, neurodevelopmental, and neurodegenerative diseases.
The mechanisms connecting the MGBA with the DMHR abound! And we explore them all, including myelination, synaptogenesis, neural plasticity, neurogenesis, hormones, neuropeptides, gut peptides, short-chain fatty acids, BDNF, and the guardians of the brain—the mighty microglia. These mechanisms operate within an intricate symphony to orchestrate and influence our psychological states, moods and emotions, social behavior, stress experience, resilience, cognitive processes, dietary intake behaviors, and mental health outcomes. See the NP 120 Part II Course flyer here.
Upon successfully completing NP 120 Parts I and II, you will embark on an enlightening journey that will equip you with the necessary expertise to delve further into this burgeoning frontier.












NP 120 Part II
Microbiome and Mental Health
Course Introduction
Note: NP 120 Part I, Microbes in Our Gut: An Evolutionary Journey into the World of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis and DMHR, is a prerequisite for this course.
Your NP 120 Part I journey began with Hippocrates‘ famous dictum, “All diseases begin in the gut.” You’ve established the foundational knowledge in the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis (MGBA) needed to progress to this course, NP 120 Part II, where you learn about the MGBA’s complex interconnection with the diet-mental health relationship (DMHR).
You’ve already explored the evolution and historical development of the MGBA and detailed the research methods contributing to its understanding. Your knowledge extends into the major physiological systems underpinning the MGBA-DMHR, gut microbiota composition and diversity, and the importance of the gut barrier in influencing and regulating the immune system, gastrointestinal homeostasis, and intestinal permeability.
This groundwork from NP 120 Part I sets the stage for NP 120 Part II, which deepens your understanding of the precise mechanisms through which the MGBA-DMHR influences mood, behavior, social functioning, psychological experience, eating behavior, and the development of psychiatric and neurological conditions. Some of these mechanisms include myelination, synaptogenesis, neural plasticity, neurogenesis, microglia, blood-brain barrier, intestinal barrier, vagus nerve, the HPA axis, neuropeptides, gut peptides, short-chain fatty acids, BDNF, and hormones.
NP 120 Part II begins by delving into the impact of diet on the MGBA-DMHR, exploring the effects of diet on the integrity of the gut and brain barriers, the production of signaling molecules (neurotransmitters, hormones, and cytokines), and the communication pathways between the gut and the brain. You’ll explore the impact of your various food components and dietary intake patterns on the composition and functioning of the gut microbiota and communication within the MGBA.
You’ll then revisit the question, “Can mental illness begin in the gut?” To answer this question, you’ll be introduced to the concept of developmental programming and learn about your gut microbiota’s ability to shape and influence your brain development and function and, thus, your mental health throughout your lifespan. You’ll explore how your early-life experiences, brain development, and gut microbiota change intertwine to influence aspects of your behavioral and psychological functioning to influence clinical mental health outcomes.
Consistent with the relationships typically explored within nutritional psychology, you’ll delve into the interconnection between your microbiota and your dietary intake behavior, including how MGBA-DMHR influences your dietary choices and underlying motivations to eat. This includes the interconnection between MGBA-DMHR and eating disorders, addiction-related behaviors, and homeostatic, non-homeostatic, and reward-related dietary intake behaviors.
Your NP 120 Part II MGBA-DMHR journey concludes with a review of potential therapeutic interventions and the development of gut microbiota-based nutritional strategies as modulators of psychological functioning. You’ll experience an exciting glimpse into the potential future advancements in this field. We hope that completing this course will help you understand new ways of understanding your own diet-related experience. Let’s begin!












NP 120 Part II
Microbiome and Mental Health
Course Information
Learning Objectives
Upon completing this course, you’ll understand how MGBA interconnects with the DMHR to influence psychological functioning, human behavior and cognition, and mental health. Upon completing this course, you will be equipped to understand and incorporate new research findings into your awareness and professional training. Upon completing this course, you’ll able to:


-
List two ways Western Diet influences the MGBA-DMHR
- Define developmental programming and describe the role of early colonization of gut microbiota in its implementation
- Describe the connection between early-life stress (ELS), the MGBA, and later-life mental health health
- Define non-digestible carbohydrates (NDCs) and describe their beneficial impact on gut microbiota
- Identify three major MGBA-DMHR bidirectional communication pathways underpinning the pathophysiology of clinical disorders
- Explain the role of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) in the pathophysiology of anxiety disorders
- Define prebiotics and explain their mechanisms of action in fostering beneficial gut microbiota and the MGBA-DMHR
- Formulate two evidence-based recommendations for a healthy diet that supports a balanced gut microbiota
- Describe the role of MGBA-DMHR in the hedonic (non-homeostatic) regulation of dietary intake behavior
- Describe the role of MGBA in modulating reward pathways and cravings associated with addictive behaviors
- Describe the role of MGBA in the hedonic regulation of dietary intake behavior
-
Explain two key mechanisms involved in MGBA-DMHR regulation of stress response and resilience
-
Formulate two evidence-based recommendations for dietary intake that support the MGBA-DMHR
NP 120 Part I is a mandatory prerequisite for this course. While NP 110: Introduction to Nutritional Psychology Methods is not, it is helpful to have the foundation in NP established, including all the terms, language, concepts, and methods in nutritional psychology.
Logistics
NP 120 Part II is online, self-paced, and composed predominantly of text, figures/diagrams, voiced powerpoint presentations, and one animated video (in Module 6). This course provides 21.25 hours of continuing education credit (CE/CPE) for licensed professionals (1hr instruction = 1 CE/CPE). NP 120 Parts I and II combined include over 445 professionally-illustrated figures, 22 voiced powerpoints, and 218 lightbulb moments (short evidence-based factoids) to enhance learning.
Once enrolled, you will have full online access to this course for four (4) months (120 days). This course is fully self-contained, and no additional materials are needed for its completion. This course must be completed in its entirety to receive course credit and a Certificate of Completion. No partial credit is given. This course is not downloadable. However, for each module, you may download a Module Download Kit containing all of the terms & definitions, figures, lightbulb moments (short evidence-based factoids), and references in APA format.
Voiced powerpoints: Please note that each module contains 2-3 sections that can be read in text version or viewed in voiced video format. The videos provide an additional learning format to add interest and lower reading requirements. The module Table of Contents indicates which sections are provided in video format, which is indicated by the word (video) next to the section. The module section itself will also have a note reminding you of this video versus text option.
This course has a syllabus, four modules, four quizzes, one final exam, and a course evaluation. The pace with which you complete this course will depend on your personal reading, comprehension, and learning style. Depending on which type of learner you are, the estimated component lengths of these course modules are the following:


Who is this course for?
Prerequisites
NP 120 Part I is a prerequisite for this course! While NP 110: Introduction to Nutritional Psychology Methods is not a prerequisite for this course, graduates of NP 110 will have a better command of DMHR/NP language, concepts, and methods, which may benefit their learning in NP 120 Parts I & II. To receive an Introductory Certificate in Nutritional Psychology, you must have completed in its entirety all four NP courses, including NP 110, NP 120 (Parts I & II), and NP 150.
Scope of Practice
This course presents evidence, knowledge, and conceptual learning (psychonutritional education) on how MGBA (and diet) influence all aspects of the diet-mental health relationship within nutritional psychology. This course is not designed to provide diagnosis, nutritional, or therapeutic intervention outside of one’s existing professional scope of practice. This course does not provide the following:
- Guidelines for incorporating assessment, diagnosis, or interventions into clinical practice
- Materials for dietary recommendations or nutritional/mental health interventions
- A method for weight loss or weight control, or a “cure” for clinical mental health disorders
- A license to practice nutritional or psychological interventions or provide medical advice
This course does provide the following:
- Proficiency in interpreting MGBA-DMHR research, enabling critical thinking and evidence-based decision-making
- The skills to effectively communicate and educate others about the psychonutritional aspects of the MGBA-DMHR, empowering individuals to make informed dietary choices to support mental health
- Awareness of the factors influencing the MGBA-DMHR, including lifestyle, stress, and environment
- Knowledge of emerging research and advancements in microbiota-based interventions, including probiotics, prebiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation, providing insights into innovative mental health treatment and prevention approaches
- The opportunity to network and collaborate with experts, researchers, and professionals in the study of MGBA-DMHR, facilitating interdisciplinary dialogue and the exchange of ideas
Q&A
NP 120 Part II Course Q&A's
A: Yes, this course is taught fully online through the CNP website and can be completed at your own pace.
A: Yes, NP 120 has open enrollment, and you can begin any time.
A: NP 120 Part II is estimated to take 21.25 hours to complete, depending on your learning style and previous experience in nutrition and psychology and whether you've taken NP 110. If this information is new to you, or you are a deep learner, it may take more time to complete.
Proper NP 120 citation format: Author(s) (last name, first initial). (Year retrieved). Module Number: Module Title; Section Title (e.g., Module 1: The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. In (Ed.), Course title. Publishing organization. Web address.
Example:
Behairy, S., Pervaiz, N., Soliman, Y. (2023). Module 4: Communication pathways in the MGBA-DMHR. In E. Lu (Ed.), NP 120 Part I: Microbes in our gut: An evolutionary journey into the MGBA-DMHR. The Center for Nutritional Psychology. https://www.nutritional-psychology.org/np110/
A: Yes, a brief description of nutritional psychology is published in: Elsner, F., Matthiessen, L. E., Średnicka-Tober, D., Marx, W., O'Neil, A., Welch, A. A., Hayhoe, R. P., Higgs, S., van Vliet, M., Morphew-Lu, E., Kazimierczak, R., Góralska-Walczak, R., Kopczyńska, K., Steenbuch Krabbe Bruun, T., Rosane, B. P., Gjedsted Bügel, S., & Strassner, C. (2022). Identifying future study designs for mental health and social wellbeing associated with diets of a cohort living in eco-regions: Findings from the INSUM expert workshop. International journal of environmental research and public health, 20(1), 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010669












NP 120 Part II
Microbiome and Mental Health
Module Overviews
In this learning journey, we pose questions, present evidence, and impart knowledge. We do this with a vision that alludes to the infinite potential explanations for how our microbiota gut-brain axis (MGBA) and diet-mental health relationship (DMHR) interconnect.
This two-part course introduces the first evidence-based conceptual model linking the microbiota gut-brain axis to the diet-mental health relationship.
Module 5: Diet and the MGBA-DMHR
Module 5 explores how various food components, including macronutrients, micronutrients, antioxidants, food additives, and alcohol consumption, influence the composition and function of the gut microbiota. A particular focus is placed on carbohydrates and their classifications within the MGBA-DMHR framework.
Module 6: Mechanisms Underpinning the MGBA-DMHR
This module examines the evolution of gut microbiota, early life stress, and early nutritional programming and its influence on mental health. We emphasize the role of the gut microbiota as a key regulator of brain development, elucidating how microbial metabolites and signaling molecules can impact neurodevelopmental processes and influence mental health in later life.
Module 7: MGBA and the Diet-Mental Health Relationship (DMHR)
This module expands on our understanding of the pathways mediated by the MGBA that contribute to the development and progression of major mental disorders, including anxiety disorders, mood disorders, psychotic disorders, neurodevelopmental disorders, behavioral disorders, neurocognitive disorders, and subclinical experiences.
Module 8: MGBA and Behavior
This module delves into the intricate mechanisms through which MGBA pathways regulate food intake and addiction behaviors. We focus on disorders such as Anorexia Nervosa (AN), Bulimia Nervosa (BN), Binge Eating Disorder (BED), and Night-Eating Syndrome (NES), as well as Substance Use Disorders (SUD).












Microbiome and Mental Health












MODULE TABLE OF CONTENTS





Microbiome and Mental Health
Module 5: Diet and the MGBA-DMHR
Module 5 explores how various food components, including macronutrients, micronutrients, antioxidants, food additives, and alcohol consumption, influence the composition and function of the gut microbiota. A particular focus is placed on carbohydrates and their classifications within the MGBA-DMHR framework. These classifications encompass digestible and non-digestible carbohydrates (NDCs), microbiota-accessible carbohydrates (MACs), and their role in the production of the essential microbial byproducts —short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). We explore how different dietary patterns and popular dietary trends, such as the Mediterranean, vegetarian/vegan, Western, and Ketogenic diets, affect the composition and function of gut microbiota. We examine the impact of hyper-palatable foods on the gut microbiota, as well as the potential consequences of dietary changes on microbial functions and their subsequent impact on our gut health and overall well-being.
Estimated time to complete:
5.0 hours
Module Quiz
20 questions/30 min
Overview
Terms and Definitions
introduction
Food Components and Gut Microbiota
- Macronutrients and Gut Microbiota
- Carbohydrates
- Digestible carbohydrates (starch, sugars)
- Non-digestible carbohydrates (dietary fiber) (video)
- Microbiota-accessible carbohydrates (MACs)
- Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs)
- Prebiotics
- Proteins
- Fats
- Carbohydrates
- Micronutrients and Gut Microbiota
- Vitamins
- Fat-soluble vitamins
- Vitamin K
- Vitamin D (video)
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin E
- Water-soluble vitamins
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin B Complex
- Fat-soluble vitamins
- Minerals
- Iron (Fe)
- Zinc (Zn)
- Calcium (Ca)
- Magnesium (Mg)
- Vitamins
- Antioxidants and Gut Microbiota
- Polyphenols
- Akkermansia muciniphila (A. muciniphila)
- Polyphenols
- Food Additives and Gut Microbiota (video)
- Artificial Sweeteners
- Artificial food colorants
- Flavor Enhancers
- Alcohol use and gut microbiota
Hyper-palatable Foods and Gut Microbiota
Dietary Patterns and Gut Microbiota
- Mediterranean Diet
- Vegetarian and Vegan Diets
- Western Diet
- Ketogenic Diet
Conclusion
Quiz
Module references available












MODULE TABLE OF CONTENTS





Microbiome and Mental Health
Module 6: Mechanisms Underpinning the MGBA-DMHR
This module examines the evolution of gut microbiota, early life stress, and early nutritional programming and its influence on mental health. We emphasize the role of the gut microbiota as a key regulator of brain development, elucidating how microbial metabolites and signaling molecules can impact neurodevelopmental processes and influence mental health in later life. We investigate how diet, especially during early life, can affect the gut-brain axis and impact mental well-being. We explore various strategies for manipulating gut microbiota to promote mental health, including probiotics, prebiotics, and dietary modifications. Finally, we delve into the communication pathways between gut microbiota and the brain, uncovering the bidirectional signaling mechanisms involved in the MGBA and their contribution to regulating mental health.
Estimated time to complete:
4.5 hours
Module Quiz
16 questions/30 min
Overview
Terms and Definitions
Introduction
Evolution of Gut Microbiota and Early-life Programming
- Early-life Events Influencing Gut Microbiota Establishment and Brain Development
- Gestational Age at Birth (animated video)
- Mode of Delivery
- Diet
- Maternal Diet
- Early Infancy Feeding Pattern
- Complementary Feeding and Introduction of Solid Food
- Antibiotic Exposure
- Early-Life Stress (ELS)
- Early-Life Stress and Brain-to-Gut (Top-down) Signaling
- Early-Life Stress and Gut-to-Brain (Bottom-up) Signaling
- Maternal Separation (MS) Model
- Gut Microbiota as a Key Regulator of Brain Development
- Neurogenesis
- Synaptogenesis
- Myelination
- Blood-Brain Barrier
- Microglia Maturation
- Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) Axis
- Neurotrophins and Neurotransmitters
- Neurotrophins and Neurotransmitters: Brain‐Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF)
- Neurotrophins and Neurotransmitters: Serotonin (5-HT)
Gut Microbial Diversity and Mental Health
Early Nutritional Programming, Gut Microbiota, and Mental Health
Manipulating the Gut Microbiota and Mental Health
- Germ-Free (GF) Model and MGBA
- Psychobiotics and MGBA
Communication Pathways
- Neuro-Immuno-Endocrine Signaling Mechanisms (NIESMs) and Mental Health
- The Vagus Nerve
- The Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Adrenal (HPA) Axis
- Neurotransmitters
- Serotonin and Tryptophan
- Catecholamines: Dopamine, Epinephrine, and Norepinephrine
- γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA)
- Neurotransmitters
- The Neuropeptide Y Family: Neuropeptide Y (NPY) and Peptide YY (PYY)
- Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1)
- Cholecystokinin (CCK)
- Ghrelin
- Microbiota-Derived Metabolites
- Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)
Conclusion
Module Quiz
Module references available












MODULE TABLE OF CONTENTS





Microbiome and Mental Health
Module 7: MGBA and the Diet-Mental Health Relationship (DMHR)
This module expands on our understanding of the pathways mediated by the MGBA that contribute to the development and progression of major mental disorders, including anxiety disorders, mood disorders, psychotic disorders, neurodevelopmental disorders, behavioral disorders, neurocognitive disorders, and subclinical experiences. Potential and future gut microbiota-based approaches, including dietary interventions and the addition of beneficial bacteria, are explored to modulate psychological and behavioral functioning.
Estimated time to complete:
5.75 hours
Module Quiz
20 questions/30 min
Overview
Terms and Definitions
Introduction
MGBA and Clinical Disorders
- Anxiety Disorders
- Anxiety disorders
- Role of the HPA axis in anxiety disorders (video)
- Role of BDNF in anxiety disorders
- Role of the vagus nerve in anxiety disorders
- Role of microglia in anxiety disorders
- Role of neurotransmitters in anxiety disorders
- Serotonin
- GABA
- Dopamine & noradrenaline
- Role of neuropeptides in anxiety disorders
- Role of SCFAs in anxiety disorders
- Anxiety-related disorders
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- The HPA axis and PTSD
- Neurotransmitters and PTSD
- The gut neuropeptide NPY and PTSD
- The gut neuropeptide NPY and PTSD
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Therapeutic applications
- Section Summary
- Anxiety disorders
- Mood disorders
- Major depressive disorder (MDD)
- Role of the HPA axis and stress-related pathways in MDD
- Role of the neuroimmune pathway in MDD
- Role of neurotransmitters in MDD
- Other MDD-related pathways
- Role of neurogenesis and BDNF in MDD
- Role of BBB in MDD
- Role of gut-derived neuropeptides in MDD
- Role of SCFAs in MDD
- Bipolar disorders
- Therapeutic applications
- Section Summary
- Major depressive disorder (MDD)
- Psychotic disorders
- Schizophrenia
- Neurodevelopmental hypothesis of schizophrenia
- Neurotransmitters hypothesis of schizophrenia
- The dopamine hypothesis
- The GABA-glutamate hypothesis
- The Serotonin-tryptophan hypothesis
- BDNF hypothesis of schizophrenia
- Inflammation-microglia hypothesis of schizophrenia
- Therapeutic applications
- Section Summary
- Schizophrenia
- Neurodevelopmental and behavioral disorders
- Autism spectrum disorder (ASD)
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
- Therapeutic applications
Section summary
Neurocognitive disorders
- Delirium
- Major and Minor neurocognitive disorders
- Therapeutic applications
- The role of BDNF in Alzheimer’s disease
- The role of neuroinflammation and microglial activation in Alzheimer’s disease
- The role of BBB in Alzheimer’s disease
- Neurocognitive disorder due to vascular dementia
- Neurocognitive disorder due to Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
- Neurocognitive disorder due to Lewy body dementia (LBD)
- Neurocognitive disorder due to HIV infection
- Therapeutic applications
- Therapeutic applications (video)
- Section summary
MGBA and Sub-Clinical Experience
- Mood, Emotions, and Affect
- Psychological Experience: Loneliness
- Stress and Anxiety
- Stress vs. Anxiety (video)
- Stress resilience1
- Section summary
Conclusion
Module references available












MODULE TABLE OF CONTENTS





Microbiome and Mental Health
Module 8: MGBA and Behavior
This module delves into the intricate mechanisms through which MGBA pathways regulate food intake and addiction behaviors. We focus on disorders such as Anorexia Nervosa (AN), Bulimia Nervosa (BN), Binge Eating Disorder (BED), and Night-Eating Syndrome (NES), as well as Substance Use Disorders (SUD). The homeostatic regulation of the brain's hunger-satiety pathway and the non-homeostatic regulation of food cravings and eating behavior are explored, in addition to the gut microbiota's effect on reward and motivation pathways, stress responses, mood, and eating behavior. The ways in which gut microbiota manipulation can influence eating behaviors and the development of eating disorders are discussed.
Estimated time to complete:
3 hours
Module Quiz
10 questions/30 min
Overview
Terms and Definitions
Introduction
MGBA and Behavior
- Dietary Intake Behavior and Eating Disorders
- Gut microbiota and the Brain’s Hunger-Satiety Pathway (homeostatic regulation) (video)
- The vagal-neural pathway
- The gut peptides-hormonal pathway
- The appetite-stimulant NPY
- The appetite-stimulant Ghrelin
- The appetite-suppressants GLP-1 and CCK
- Gut Microbiota Impact on Food Cravings and Eating Behavior (non-homeostatic regulation)
- Gut microbiota’s effect on reward and motivation pathways (video)
- Gut microbiota’s effect on the stress response, mood, and eating behavior
- Emotional states and eating behavior
- The HPA axis, cortisol, and eating behavior
- Gut microbiota and manipulation of eating behavior
- Influencing taste buds and food sensory perception
- Hijacking the vagus nerve signaling
- Inducing dysphoria
- Gut Microbiota and Eating Disorders
- Gut microbiota involvement in Anorexia Nervosa (AN)
- Gut microbiota involvement in Bulimia Nervosa (BN) and Binge Eating Disorder (BED)
- Gut microbiota involvement in Night-Eating Syndrome (NES)
- Gut microbiota and the Brain’s Hunger-Satiety Pathway (homeostatic regulation) (video)
- Addiction Behaviors and Substance Abuse
- Addiction and the developmental influence
- Gut microbiota and Addiction-related pathways
- Reward mechanisms and addiction
- Stress mechanisms and addiction
- The HPA axis hypothesis of addiction
- The gut peptide NPY hypothesis of addiction
- Neuroimmune mechanisms and addiction (video)
- Gut Microbiota and Alcohol Use Disorders (AUD)
- Gut microbiota and Illicit drugs (opioids and psychostimulants)
- Section summary
Conclusion
Module references available
FINAL EXAM
Course Evaluation












NP 120 Part II
Microbiome and Mental Health
Continuing Education for Professionals
Approved Psycho-nutritional Education for Licensed Psychologists, Mental Health Professionals and Dietitians


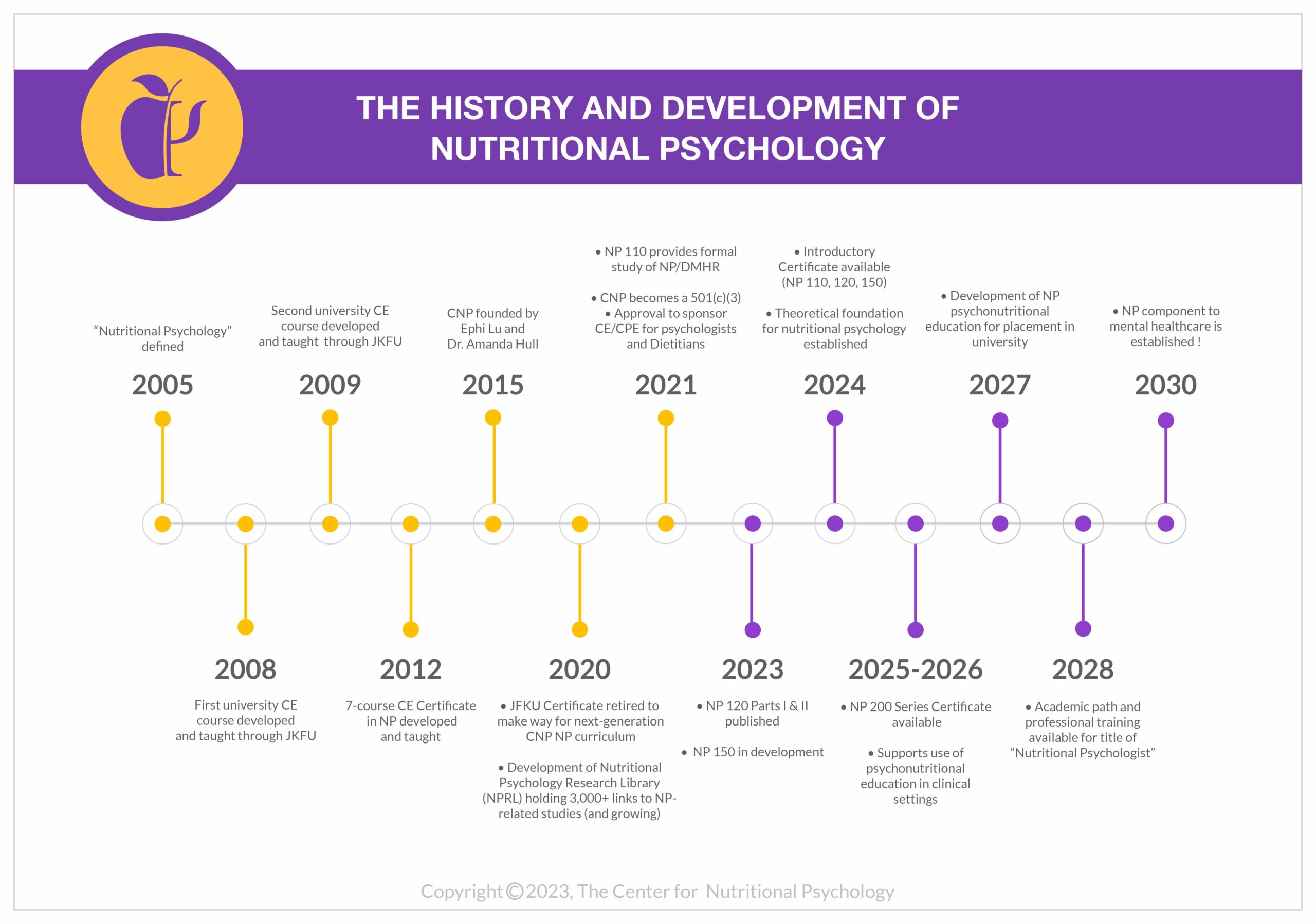
We are collecting the world’s evidence on how nutrition and the DMHR interconnect. Our courses require years of development, the consolidation of thousands of research studies, and the building of a common language and method that can support the field of nutritional psychology. Our online courses provide a solid foundation for mental health and nutrition professionals in the DMHR. As a non-profit educational organization, we are dedicated to providing an accessible online curriculum to everyone. If finances are a barrier to access, learn more about the CNP Scholarship program. Scholarship Program




CNP’s mission is to pave the way for a nutritional component to mental healthcare by 2030. Join our mission!

CNP is approved by the American Psychological Association (APA) to sponsor Continuing Education for Licensed Psychologists. CNP maintains responsibility for this program and its content.
CNP is approved by the Commission on Dietetic Registration (CDR) for licensed Dietitians to receive 21.25 CPEU through Activity Type 742 Eligible Enduring.
CNP is approved by the California Board of Behavioral Sciences (BBS) through the California Association of Marriage and Family Therapists (CAMFT Provider #1000102) to provide 21.25 CE for LMFTs, LCSWs, LPCCs, and/or LEPs.
Course Disclaimer
The information in this course is not meant to, nor should it ever be used, to treat, mitigate, or cure psychiatric illness. This information should never be used as a substitute for sound medical advice. This course is educational in nature and is designed to introduce professionals, students, and interested individuals in developing their understanding of the connection between diet and all aspects of psychological functioning and mental health. Best practices for how to integrate this information professionally, ethically, and within the standards of practice will be covered in upcoming courses. While this information can be incorporated into one’s practice within an educational framework, it cannot be used to provide dietary advice, any form of dietary intervention, or to treat any psychological or mental health issues.





