The impact of gut microbiota on the development of anxiety symptoms—A narrative review

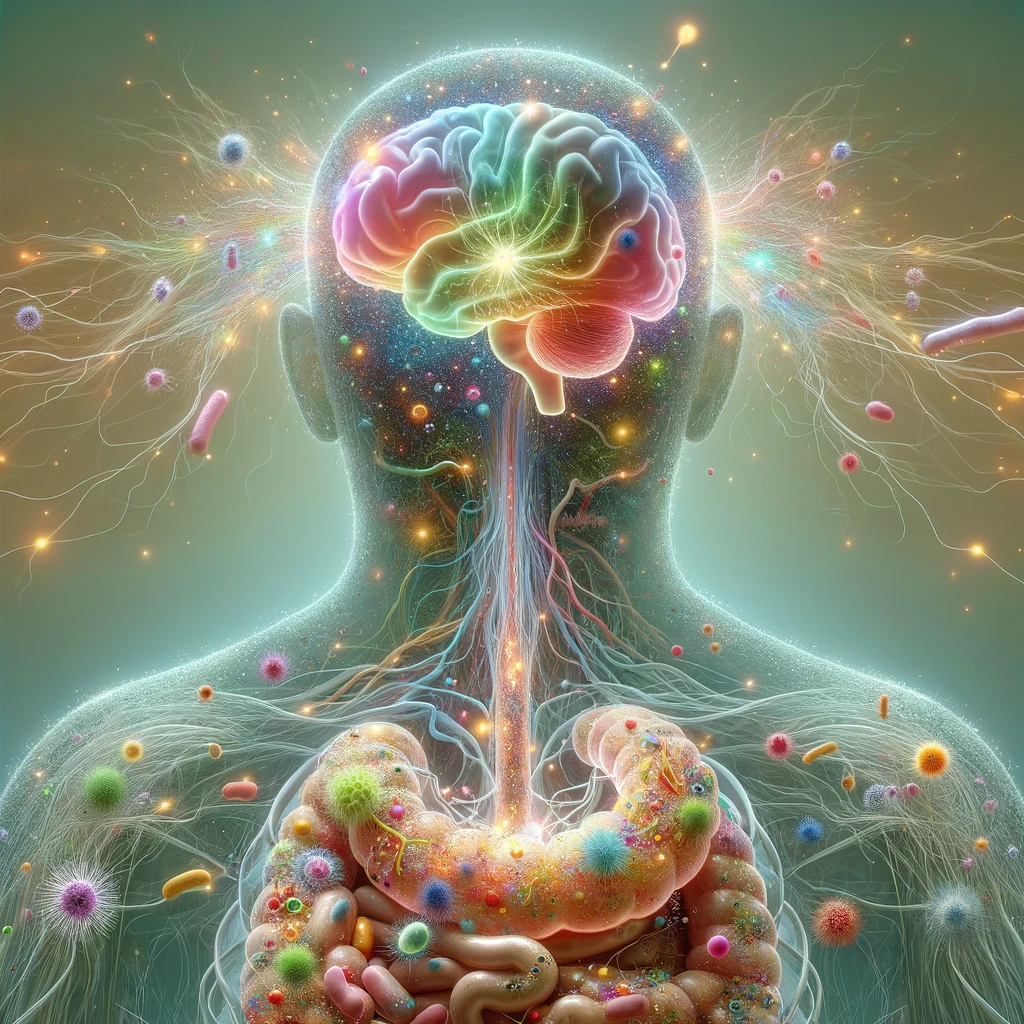
The gut microbiota plays a significant role in influencing mental well-being, with increasing research linking gut microbial imbalances to anxiety and depression. This review by Nikel et al. (2025) focuses on changes in gut microbiota composition observed in individuals with anxiety disorders and examines how probiotics may help ease related symptoms. The primary goal is to evaluate recent findings on gut-brain interactions and their relevance for mental health treatments. Using databases such as PubMed, Embase, CINAHL, and Google Scholar, studies were analyzed to assess the gut microbiota’s role in anxiety and the impact of probiotic supplementation. Findings reveal that people with anxiety frequently exhibit gut dysbiosis, marked by reduced microbial diversity and diminished levels of bacteria that produce short-chain fatty acids. Moreover, probiotics, especially strains from the Lactobacillus genus, show promise in reducing anxiety symptoms by improving gut microbial balance. Overall, gut dysbiosis is strongly associated with anxiety, and probiotic use may offer a viable therapeutic option, though more research is required to fully understand mechanisms and optimize treatments. [NPID: Microbiota, anxiety disorders, mental health]
Year: 2025
 Navigation
Navigation