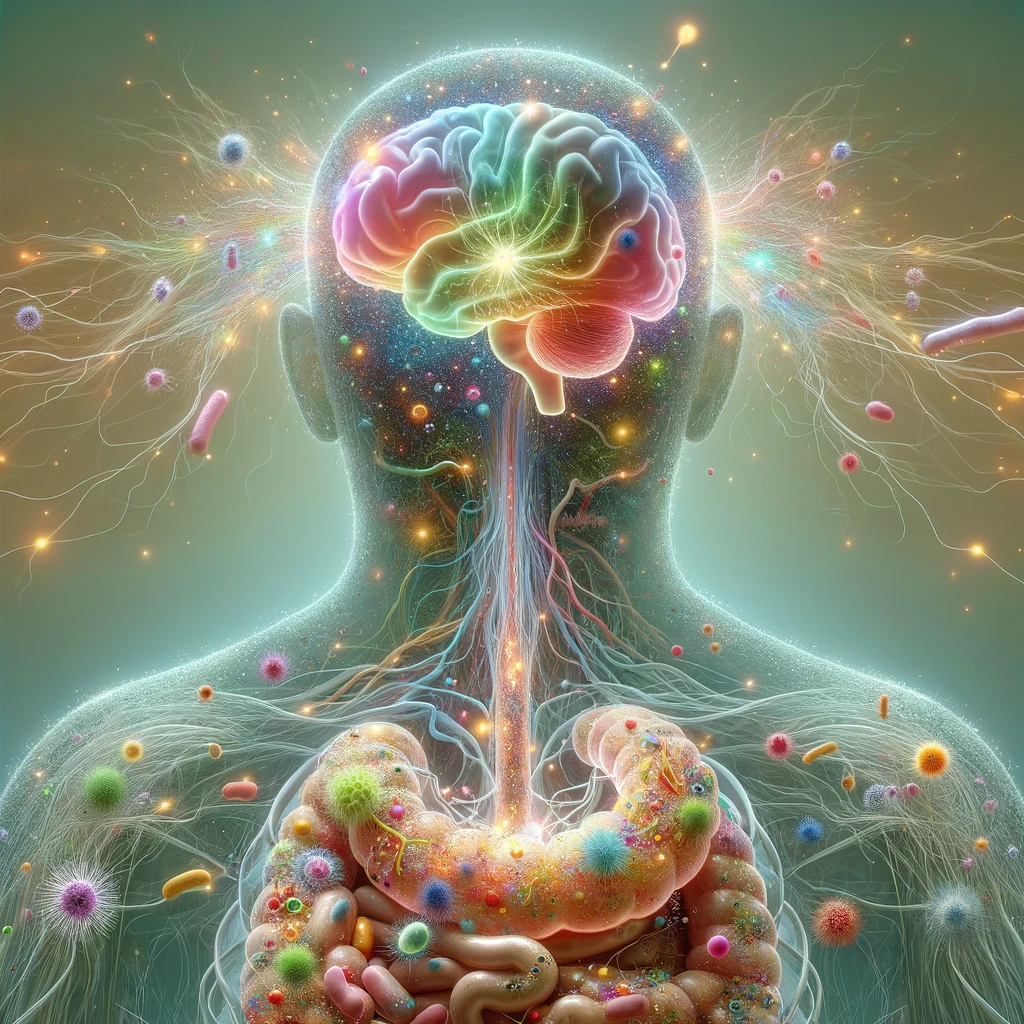
Exploring the gut-brain Axis: Potential therapeutic impact of psychobiotics on mental health
One of the most complex and debated topics in microbiome research concerns the role of gut microbial metabolism in neuropsychological disorders. Psychobiotics influence human behavior and brain functions through the gut-brain axis, which involves neural, immune, and metabolic pathways. These microbes hold therapeutic promise for treating various neurodegenerative and neurodevelopmental disorders, including depression, anxiety, autism, ADHD, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, schizophrenia, Huntington’s disease, anorexia nervosa, and multiple sclerosis. However, the precise mechanisms through which psychobiotics interact with these disorders remain poorly understood and require further study. This review by Cocean & Vodnar (2024) examines the relationship between gut microbiota and neurological or neurodegenerative diseases, exploring the potential of psychobiotics as both a preventive and therapeutic solution. It summarizes recent advancements in gut-brain axis research, highlighting the potential benefits of psychobiotics while emphasizing the need for more investigation in this field. [NPID: Gut microbiota, psychobiotics, gut-brain axis, neurodegenerative disorders, neurodevelopmental disorders]
Year: 2024
 Navigation
Navigation